Diabetes again claims highest drugs spend
In Analysis
Follow this topic
Bookmark
Record learning outcomes
The latest analysis of community prescribing in England graphically illustrates the nation's health problems and treatment priorities.
AN ANALYSIS of community prescribing published earlier this year by the Health and Social Care Information Centre (HSCIC) shows that over 1.03bn items were dispensed in England in 2013 with an average ingredient cost per item of £8.37.
These figures represent a 58.5 per cent increase on 2003 in terms of numbers of items dispensed, but a drop in average net ingredient cost (NIC) from £11.56 over the same period.
While the NIC has undoubtedly been affected by patent expiries for several widely prescribed drugs between 2003 and 2013 €“ notably simvastatin, atorvastatin, lansoprazole, amlodipine and olanzapine €“ the figures also reflect the impact of the category M scheme, which was introduced in 2005.
The overall generic prescribing rate, which has been rising steadily over the years, hit nearly 84 per cent, with the overall generic dispensing rate topping 75 per cent for the first time. However the report says this trend is unlikely to continue as €it may have reached a clinically appropriate rate for the drugs currently available€. Nine out of every 10 prescription items were dispensed free of charge.
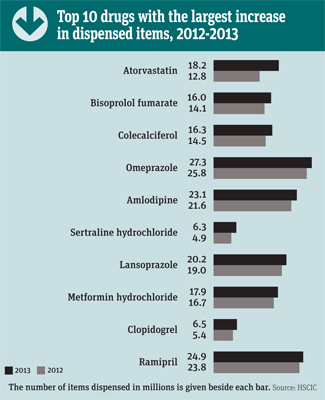 The number of items per head, on average, rose from 13 to 19 between 2003 and 2013, fuelled by a drive towards proactive disease management and preventative medicine.
The number of items per head, on average, rose from 13 to 19 between 2003 and 2013, fuelled by a drive towards proactive disease management and preventative medicine.
Other contributing factors include:
- The increasing population
- The fact that there are more older people who generally receive more prescriptions than the young
- Earlier diagnosis and treatment of conditions
- Increased prevalence of certain conditions such as diabetes
- Shifts in prescribing practice as a result of new guidance and evidence and in the duration of treatment each item is intended to cover.
Antidepressant drug costs rose by over a third from just over £210m in 2012 to £282m in 2013. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) significantly outweigh tricyclic and related antidepressants (TCAs), with the exception of amitriptyline, which is used for several other indications.
Of the SSRIs, citalopram is the most commonly prescribed, and sertraline overtook fluoxetine to become the second most dispensed drug in the class.
However, although antidepressants saw the greatest increase in prescribing volume, the leading area in terms of net ingredient cost was diabetes (for the seventh year in a row). Nearly £800m was spent on this therapeutic area in 2013. Other points of note include:
- Lipid regulating drugs are being increasingly prescribed, thanks to more widespread use of both atorvastatin and pravastatin
- There was a large increase in antiepileptic prescribing, driven by greater use of both gabapentin and pregabalin
- Analgesic prescribing went up, with paracetamol use showing a marked rise and costs spiralling due to category M
- Hypnotic and anxiolytic prescribing has fallen, with benzodiazepines far less likely to be used due to wider use of the 'Z-drugs', particularly zopiclone
- Antibacterials saw the greatest decrease in dispensed items, led by a large decrease in the use of amoxicillin.
Key facts
- Over 1.03bn items were dispensed in 2013 €“ up 3 per cent on 2012
- The overall net ingredient cost (NIC) of prescriptions has increased by just 15 per cent from £7.51bn in 2003 to £8.63bn in 2013
- Diabetes medicines once again accounted for the biggest NIC in 2013.
